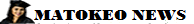Education System In Tanzania (2-7-4-3+)
The Tanzanian educational system is based on a 2-7-4-2-3+ structure. In other words; 2 years of Pre-primary school, 7 years of Primary school, 4 years of Ordinary secondary school (ordinary level), 2 years of Advanced secondary school (advanced level) and at least 3 years of Higher education.Tanzania Education Development Vision 2025
The Tanzania Development Vision 2025 states Tanzania’s education vision as: “A well-educated, knowledgeable and skilled Tanzanian able to competently and competitively cope with political, social, cultural, economic and technological development challenges at national and international levels.”Tanzania Development Vision 2025 accords high priority to the education sector, which is considered to be pivotal in bringing social and economic transformation, as described in the following statement:-
"Education should be treated as a strategic agent for mind-set transformation and for the creation of a well-educated nation, sufficiently equipped with the knowledge needed to competently and competitively solve the development challenges which face the Nation". In this light, the education system should be restructured and transformed qualitatively with a focus on promoting creativity and problems solving.
Thus, the Education system in Tanzania, including secondary education, plays a critical role in the development of the nation through continuous production of knowledgeable, creative, and problem-solving graduates.
Challanges facing the education System In Tanzania
- Shortages of teachers, especially in the sciences and mathematics, with many students not able to do these subjects at all.
- Asymmetrical deployment of teachers of required, whereby urban areas have an advantage in recruiting more and better teachers compared to rural community secondary schools, most of which have an acute shortages of teachers.
- Inequalities in learning environments among different schools resulting in inequalities of learning outcomes, with girls doing poorly in both participation rates and pass rates, especially in science and mathematics subjects, and community secondary schools doing consistently poorly.
- Insufficient infrastructure, including many construction projects which are not completed.
- Lack of, or non-use of, laboratories in most schools resulting in students doing the science theoretically, and most of them doing poorly. This poor performance in science subjects has, in turn, resulted in an avoidance syndrome, with most students choosing to enrol in social science/arts subjects, rather than natural sciences.
- Poor teaching approaches in the classroom, as it is teacher-centered, with students relying heavily on the teacher and old notes, and classroom time often not being used efficiently and effectively for mental engagement of the students.
- Low transition rates from Ordinary to Advanced Level secondary education due to limited availability of Form 5 places..
- Limited access to secondary education for nomads, marginalized groups and disabled learners.
Assessment system in Ordinary & Advance Level
Examination results for the Certificate of Secondary Education are expressed in letters, whereby the letters A through D represent a passing grade. Examination results for the Advanced Certificate of Secondary Education are also expressed in letters, whereby the letters A through E represent a passing grade (principal pass), S represents a subsidiary pass and F represents a fail.Participation in secondary education requires a Certificate of Secondary Education and an Advanced Certificate of Secondary Education.
Ordinary and Advance Level Grading System
| Certificate of Secondary Education (CSE) | Advanced Certificate of Secondary Education (ACSE) | Description |
| A | A | Excellent |
| B | B | Very Good |
| C | C | Good |
| D | D | Satisfactory |
| E | Poor | |
| F | F | Fail |
| S | Subsidiary Pass |
Higher education bachelor's degrees Grading System
| Letter | Description | Classification |
| A | Excellent | First Class |
| B+ | Very Good | Upper Second Class |
| B | Good | Lower Second Class |
| C | Satisfactory | Pass |
| E | Fail | |
| F | Fail |
EDUCATION SYSTEM IN OTHER COUNTRIES
Education System In Uganda
Education System In Botswana
Education System In Malawi
Education System In Namibia
The System Of Education In USA
OTHER IMPORTANT LINKS
MoESTMoE-Zanzibar
Utumishi
PORALG